The main components of a heat engine
With 1,659,008 registrations in France in 2021, cars remain a popular means of transport. They are part of everyday life, regardless of the use made of them: personal vehicle, taxi, bus, truck, tractor... Their ability to move is essentially based on one main part: the engine. There are several models, the most common of which is the combustion engine. Every car enthusiast has already wondered about the composition of this system. So, what are the parts that make up a heat engine? How to proceed in case of replacement?
The heat engine: how does it work exactly?
It is the central part of a motorized vehicle. Still called internal combustion or explosion engine, it is still very present on the majority of cars used in the world. Its particularity lies in the use of hydrocarbons for propulsion. This mode of operation is opposed to that of electric motors, which operate solely thanks to a coil of electric wires, a stator and a rotor.
There are several important pieces of information to know regarding the classification of a heat engine. These include, among others:
All these parameters must be taken into consideration to replace the engine of your car with a used engine when a malfunction is found. In this regard, the engine of a car is very expensive, turning to second-hand models can be a wise solution.
Endothermic, exothermic, petrol and diesel engines
Regarding the place of combustion of engines, only those of the endothermic type are used in the automotive industry. These are where combustion takes place inside the engine, rather than outside. The second mode of operation is more specific to exothermic engines. They are used for steam engines among others.
The classification of engines according to the fuel used and the type of ignition makes it possible to define two sub-categories: Otto engines and those of the Diesel type. The former use gasoline as fuel and ignition is by spark.
Also called internal combustion or controlled ignition engines, they require the presence of a mixture of air and gasoline. The latter will ignite immediately as soon as an electric spark is produced by the ignition system. Note that this type of engine has the particularity of supporting moderate pressures. This makes it capable of reaching a high number of revolutions and a maximum power between 5500 and 7000 revolutions per minute.
Diesel engines still known as "compression ignition engines" use diesel instead to operate. Combustion is initiated by the ignition of the fuel. This is done through fine spray injection at high pressure, in a very high temperature and highly compressed space.
To hold up in this highly pressurized environment, the parts have to be very heavy and sturdy. This usually limits the number of revolutions per minute such an engine can achieve. However, two types of diesel engines can be defined based on the number of revolutions per minute.
These are the fast diesels and the slow ones. The former are capable of reaching 5,000 revolutions per minute and are generally fitted to cars for personal use and certain light commercial vehicles. Slow Diesel engines are more intended for trucks, buses, locomotives, ships. The number of revolutions reached is between 900 and 2000 revolutions per minute.
The other characteristics of a heat engine
Heat engines are of the volumetric type. This means that the moving elements inside generate variable volumes depending on their movements. There are two types: reciprocating and rotary.
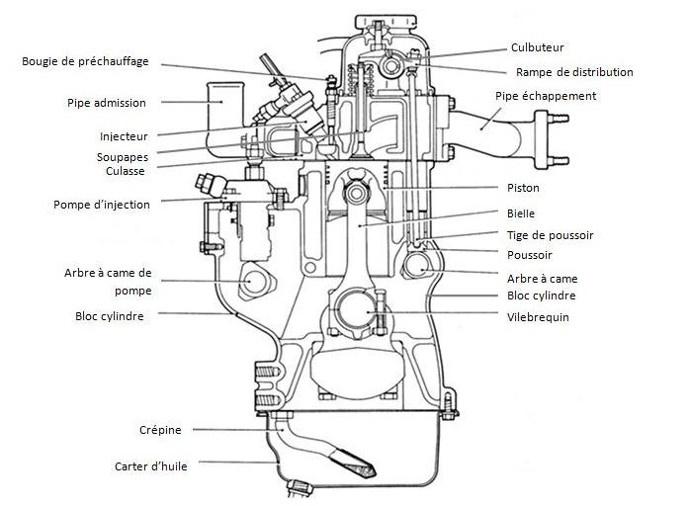
The first are composed of cylinders in which pistons alternate between linear and rotary movements. They are widely used in the automotive industry. On the other hand, rotary engines are much less so. They operate using pistons with rotating triangular sections.
Regarding the number of cycles, we will mainly talk about 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. 4-strokes follow the following stages: intake, compression, rebound and explosion. On the other hand, two-stroke engines complete the full cycle faster.
The piston performs only two strokes and one revolution of the crankshaft, against 4 strokes and 2 revolutions with the first type of engines. This makes those 2-strokes more powerful than their competitors. Nevertheless, 4-stroke engines will be used for automobiles while the others will be fine for water vehicles, motorcycles, and industrial machinery.
Finally, the engines are single-cylinder or multi-cylinder: composed of a single cylinder or several. The arrangement of these elements is also important: linear, in V, in W, with opposite horizontal cylinders.
The components of a heat engine
The heat engine is a very complex structure made up of several blocks. These include: the heart of the engine, air intake, fuel supply (injection), ignition, exhaust, cooling and lubrication.
The heart of the engine
It is made up of several main parts, namely:
This set of elements allows the propulsion of the vehicle, its management and its piloting. It is the central part of an automobile.
admission
The composition of this block comes with a throttle body, an air compressor, an air filter and a manifold gasket. The function of this module is to allow air to enter the engine, so that the mixture with the gasoline occurs and the combustion also. The amount of air entering is regulated by the throttle body which is linked to the throttle. The air filter is used instead to purify the incoming air so as not to interfere with the operation of the engine.
ignition
It contains parts such as alternator, ignition coil, starter, engine computer, rotary switch, glow plugs, spark plugs, battery and alternator pulley.
The main function of the ignition block is to produce the spark necessary for combustion. Initially, the battery supplies current to the coil. It too will transmit a strong current to the spark plugs and ignition occurs.
Injection
At the injection level, there are the following modules:
Injection is essential in an engine, because it allows the delivery of fuel to the combustion chamber. When it works well, hydrocarbon consumption is reduced and the engine is more efficient. In addition, CO2 emissions are also reduced.
The exhaust
In general, there is a catalyst, an exhaust silencer, a lambda probe, a tube and a bag collar of the EGR valve. The function of this block is to remove combustion gases. For this, they are first conveyed to the rear of the vehicle, then expelled into the air. In addition, it serves to absorb the noise produced by the engine. This is why a very noisy vehicle is a symptom of a fault in the exhaust system. These failures can lead to problems with the various component modules and the engine itself.
cooling and lubrication
The parts that make up this system are a calorstat, a dry sump, an oil strainer, a hose, an oil filter, an oil dipstick, an oil pump, the coolant, a water pump, a radiator and an oil tank.
This set of elements allows the engine to operate in the best possible conditions. It must be sufficiently lubricated and its temperature must not be excessively high (around 90°C). When it is close to 120°C, an overheating problem is suspected. It can lead to material expansion and engine malfunction.
How to replace a heat engine?
Knowing the main elements of a thermal engine is essential, especially when replacing this element. It is therefore important to choose the right engine to buy to avoid unpleasant surprises. Two main references are very useful for this purpose.
The engine code
Before purchasing one, it is necessary to ensure that the one you are targeting is identical to the one to be replaced. It is therefore recommended to use the engine code so as not to be mistaken. It is a sequence of numbers and letters that identifies a model used for the automobile to be repaired. This code can be found in box D2 of your vehicle registration card or on the vehicle identification sheet.
At the level of the car itself, the code is accessible in several places for models produced from 1997 or 1998. It is visible at the level of the engine block, under the timing cover, in the trunk of the car or in the spare wheel compartment.
It may happen that you are unable to find the engine code. In this case, another identifier is just as useful to find the engine you need and the other spare parts that may be needed.
The VIN: Vehicle Identification Number
Also called "chassis number", it is an alphanumeric series allowing the manufacturer to identify a vehicle. It also makes it possible to determine the options installed, the parts used or the color of the vehicle thanks to the paint codes. You can also discover the history of this vehicle, the list of its owners and many other essential information.
To find the chassis number, consult the gray card of your car, more precisely at point E. It is made up of 17 characters that can also be found on the car in several places: the chassis (engraving by typing cold), the windscreen, the manufacturer's plate.
The last element mentioned is generally located under the hood or on the side of the door. By the way, the VIN can also be accessed from the on-board computer of newer cars.
The structure of the chassis number is rather particular. The first 3 characters are used to identify the manufacturer and possibly the place of production of the vehicle. This is the “World Manufacturer Identification”. It is specific to each manufacturer and standardized. Some manufacturers may have more than one depending on where their cars were made. This is the case, for example, of Ford, which produces its vehicles in Germany and Spain.
The six characters following the WMI form the VDS: Vehicle Descriptor Section. This sequence of characters makes it easy to identify the model, the type of bodywork, the engine. Its structure is specific to each vehicle manufacturer. So, it is not possible to use certain precise characters to draw the same conclusion with all marks. Proceeding on a case-by-case basis is recommended.
The remaining part of the VIN forms the VIS. Also called “Vehicle Identifier Sector”, it reveals information specific to the vehicle only. This is data that specifically identifies this vehicle, as well as the parts that were used in it during assembly.
Engine purchase and replacement
Go online and find a parts dealer. Enter the engine code in the search bar. This is essential to ensure compatibility between the products offered and those of your car.
To purchase additional engine parts, use the VIN instead. To do this, make sure that the trader has a chassis number decoder on his site. If so, insert the alphanumeric sequence into the decoder, select the engine corresponding to your needs, then make your purchase.
It is recommended to bet on a second-hand engine with a fairly low mileage. Depending on your purchasing power, you can choose between the following ranges:
This type of engine is generally more accessible than its completely new equivalent. It is also possible to buy refurbished equipment. These are engines that have the particularity of having been completely rebuilt.
With regard to the selection of the used spare parts sales platform, certain precautions must be taken. To obtain good quality modules at an affordable price, make sure that the products marketed come from a network of automobile dismantlers. Bet especially on a supplier of parts that offers a guarantee of at least 6 months. This protects you in the event that the purchased product develops any faults.
Likewise, make sure that the chosen merchant is able to deliver to you within 48 to 72 hours maximum. This is essential to complete the repair of your vehicle and benefit from it again as soon as possible. Once your engine arrives, it is recommended to have it installed by a mechanic.








